First, some background: What is an NSAID?
NonSteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) such as phenylbutazone (Bute), flunixin meglumine (Banamine) and firocoxib (Equioxx) are commonly used in equine patients to help relieve pain, decrease inflammation, and control fever.
Written By: Lauren Alderman, DVM, CVA, CVSMT
How does an NSAID work?
NSAIDs work by interfering with the production of prostaglandins, a family of chemicals responsible for promoting inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a normal process and necessary for healing, but it can also lead to pain and fever.
What are the risks?
In addition to their involvement in pain and fever, prostaglandins have several other important functions in the body. These include promoting blood’s ability to clot and protecting the lining of the stomach from its acidic contents. Because NSAIDs interfere with production of helpful prostaglandins along with those responsible for pain and fever, their use does carry a risk of potentially harmful side effects.
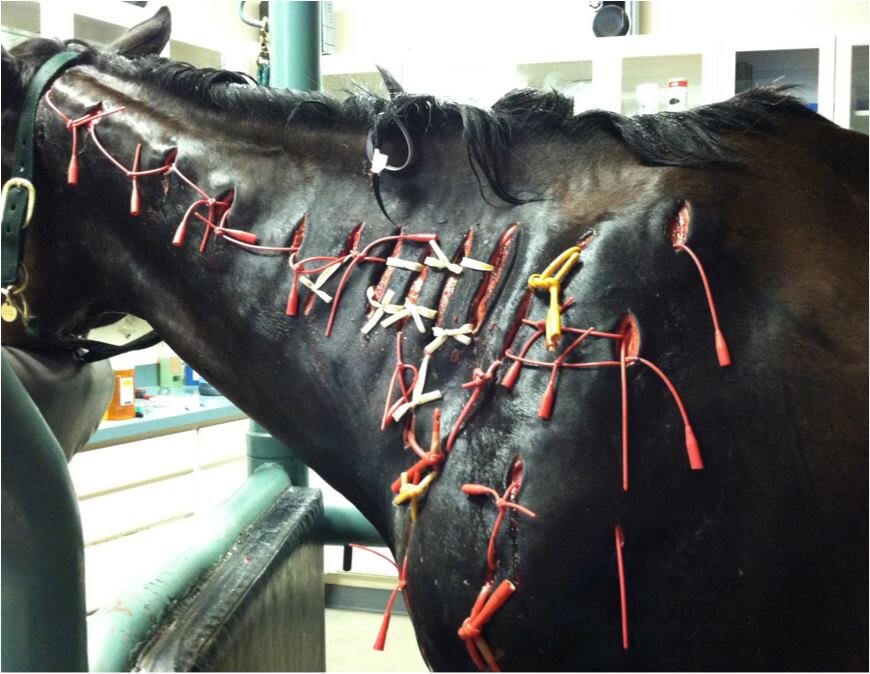
In horses, the most common side effects we encounter include the formation of ulcers in the stomach and gastrointestinal tract, colitis, and kidney failure. Chronic (long-term) use of these medications, or use in dehydrated patients, can increase the likelihood of these adverse effects. Injectable forms of phenylbutazone and flunixin meglumine should only ever be administered intravenously, as injection outside of a blood vessel (for example, accidentally giving a dose in the muscle or inadvertently injecting just outside the targeted vein) can lead to devastating, sometimes fatal tissue damage and infection.
Horse being treated for clostridial myositis following an intramuscular banamine injection.
Which NSAID is right for the job?
All of the NSAIDs discussed in this article require a veterinary prescription, and your veterinarian will help you choose the best medication, dose, and treatment duration for your horse. Phenylbutazone is available in oral and injectable (intravenous) formulations. It is commonly prescribed to reduce musculoskeletal pain and inflammation. Flunixin meglumine is also available in oral and injectable (intravenous) formulations. This medication is often used to control fever or colic pain, and is also beneficial in reducing ocular (eye) pain and inflammation.
Firocoxib is also available in both oral and injectable (intravenous) formulations. As with phenylbutazone, this medication is commonly prescribed to reduce musculoskeletal pain and inflammation. Firocoxib differs slightly from the other NSAIDs discussed here in that it interferes with the prostaglandin production process in a more selective way. The result is that firocoxib carries a decreased risk of adverse gastrointestinal side effects. For this reason, some veterinarians choose this medication for horses with a history of gastric ulcers, or for those requiring a longer course of treatment.
Shop for NSAIDs on our online pharmacy!