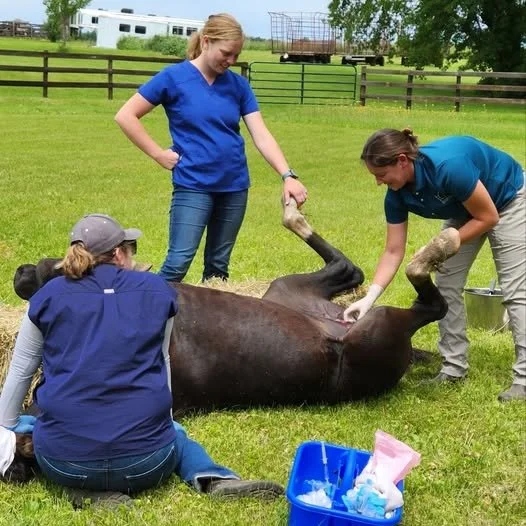
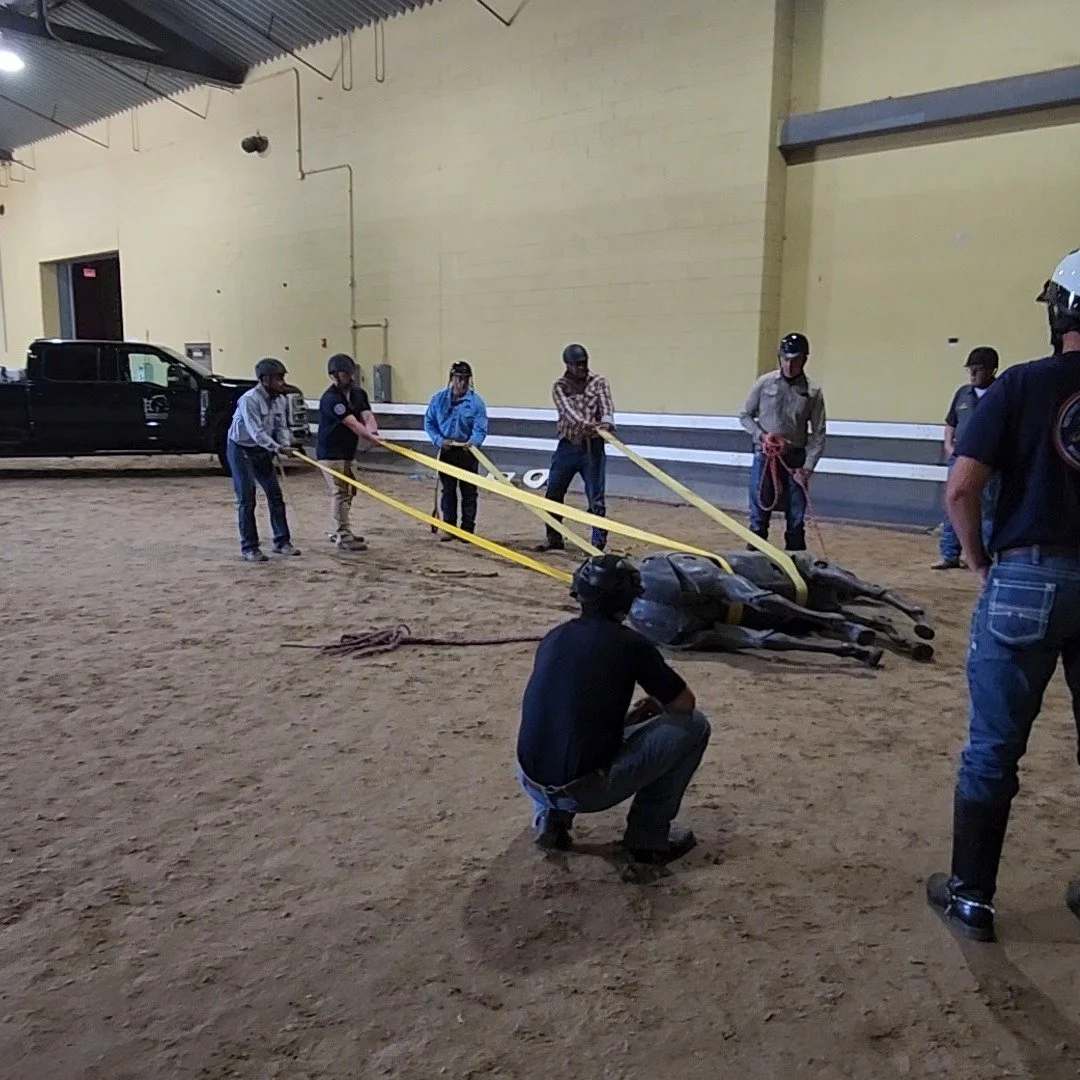
Colic is the common word to describe abdominal pain in horses. Typically, colic is related to an issue involving the digestive tract - stomach, small intestines, cecum, large colon, or small colon.
Everything You Need to Know About Laminitis
Laminitis can be defined as inflammation of the laminae that anchor the coffin bone within the hoof capsule.
Another term that may be encountered in discussions about laminitis is founder, which refers to the rotational and downward movement of the coffin bone within the hoof capsule. This sometimes occurs in severe cases of laminitis due to the breakdown of these crucial laminar attachments.
Potomac Horse Fever & Mayflies
EHV-1 and Protecting your Horse During Show Travel
EPM and How to Prevent it
Equine Protozoal Myeloencephalitis (EPM) is a neurologic disease in horses caused by infection with the protozoan Sarcocystis neurona (SN). SN infects horses when they ingest the organism in contaminated feed or water. The definitive host of this organism is the opossum, which passes the organism in its feces.
What To Do About Colic
Potomac Horse Fever: The Newest Threat in the Midwest
Previcox vs. Equioxx
Previcox and Equioxx are the same active ingredient, in different forms for oral use. While Previcox was significantly less expensive than Equioxx, it was not available for equine use. Read on to understand why. However, Equioxx now comes in a tablet form. Contact your veterinarian for more information.
Genetic Conditions and Testing
A lot of the diseases you know of actually have a genetic basis. The 11 that are regularly tested for are Hyperkalemic Periodic Paralysis (HYPP), Polysaccharide Storage Myopathy (PSM), Malignant Hyperthermia (MH), Grey Horse Melanoma, Recurrent Exertional Rhabdomylosis (RER), Hereditary Equine Regional Dermal Asthenia (HERDA), Lavendar Foal Disease, Cerebellar Abiotrophy (CA), Glycogen Branching Enzyme Deficiency (GBAD), Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID), and Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa (JEB)